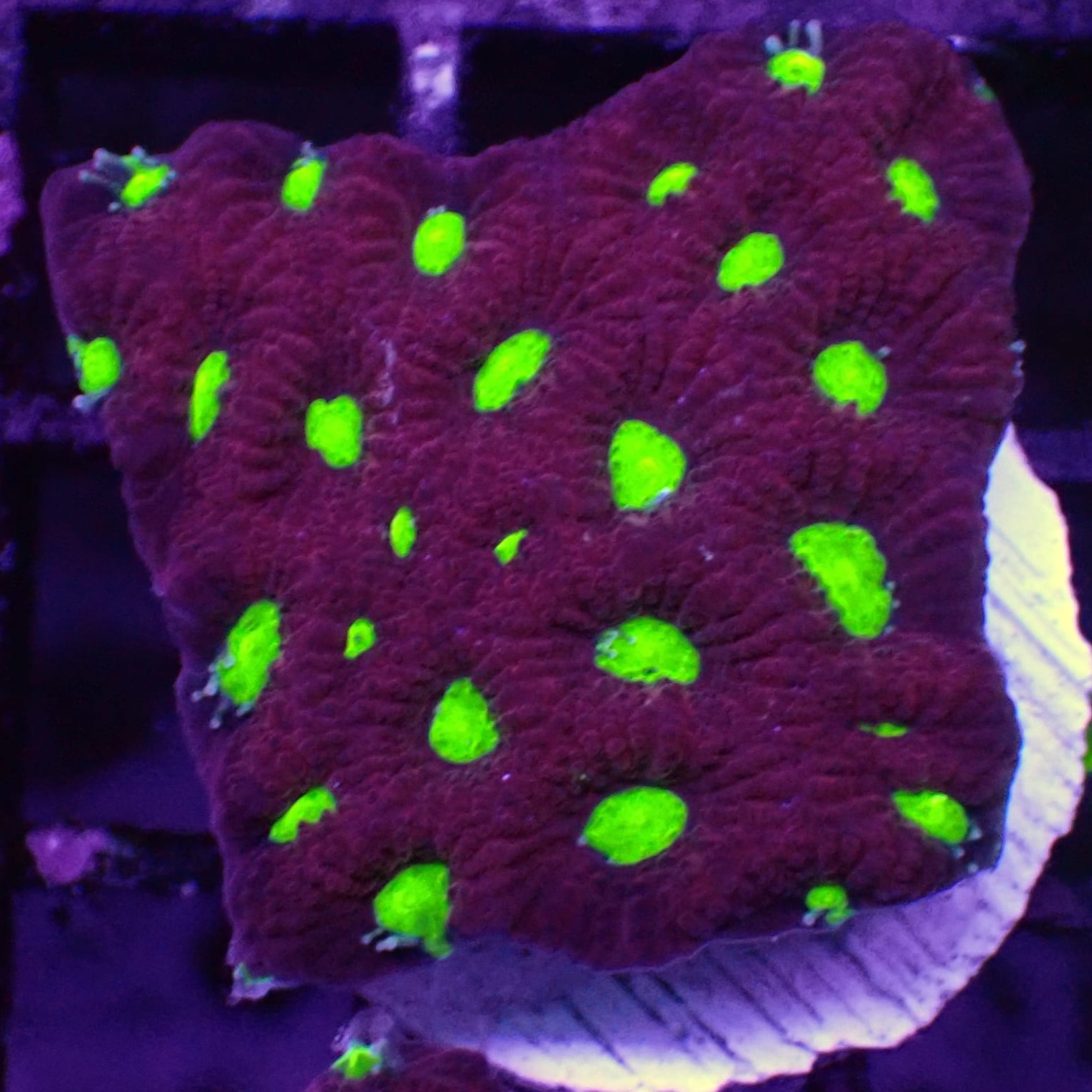
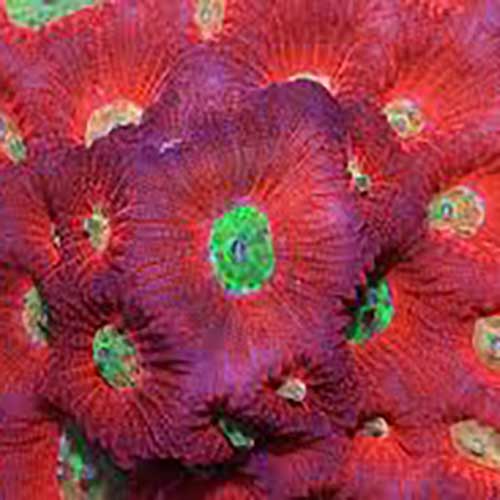
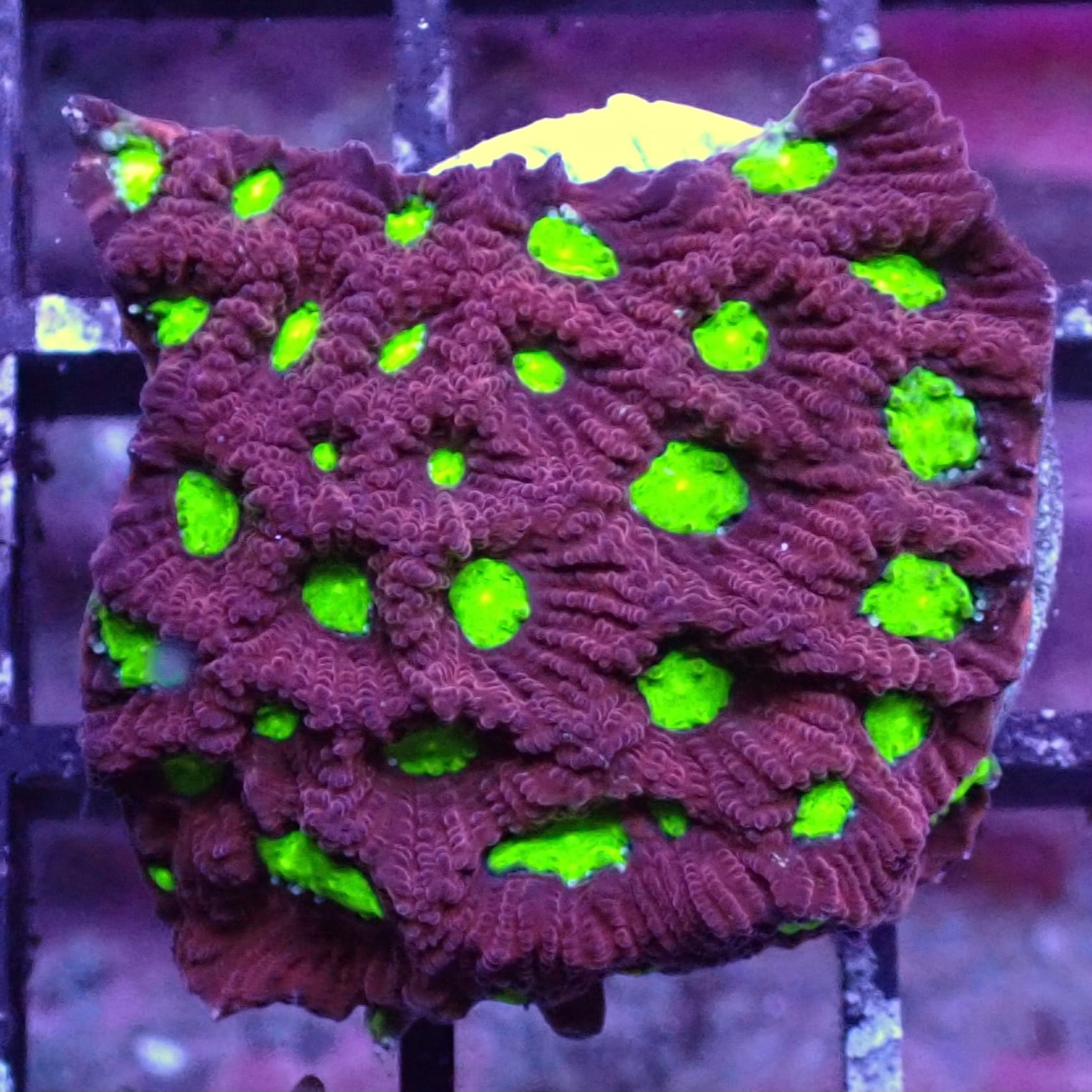
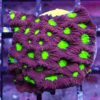
, includeRed Green Eye Favia corals feature vivid green eyes on a red textured surface. Their polyps form tight, maze-like patterns. Favias can display an array of captivating shades. The diversity in colouration is truly remarkable, since both genetics and the environment play significant roles in determining appearance.
Please note that the images displayed on our website are intended as a guide only. We have done our utmost to provide the closest representation possible for this type of coral, to help give an idea of what to expect. Corals are living organisms that can exhibit significant variation in colour and appearance due to a range of environmental and genetic factors. For example, the following are a few examples of conditions that can influence how corals look:
- Lighting: The brand, spectrum, intensity, and duration of light play a major role in how corals display their colours.
- Transit: Corals may change colour after being moved. They may either regain their original appearance or adapt to suit their new environment.
- Water Chemistry: Elements such as pH, salinity, and trace minerals can subtly or significantly alter a coral’s appearance.
- Nutrition: The availability and type of nutrients can affect both colouration and growth.
With this in mind, please be aware that actual specimens may differ in appearance.
Defining Characteristics.
Favia corals can be identified by their maze-like polyp structure and shared walls between polyps. They are often confused with Favites corals, but Favites have larger, more individual polyps with their own walls.
Taxonomy.
Favia corals belong to the family Mussidae. Their closest relatives include corals from the genera Favites and Goniastrea. The genus Favia used to include over 100 different species but most of them have now been reclassified into genera Favites and Goniastrea. In the hobby, ‘favia’ is more an umbrella term for closed brain coral so some experimentation may be necessary when placing them.
Distribution.
Favia corals are found in the Indo-Pacific region, including the Red Sea, Indian Ocean, and the central and western Pacific Ocean.
Natural Habitat.
These corals inhabit the reef slopes and lagoons, preferring areas with moderate light and water flow.
Symbiotic Relationship.
Red Green Eye Favia corals house zooxanthellae algae within their tissues, which perform photosynthesis to produce glucose, glycerol, and amino acids. These nutrients provide up to 90% of the coral’s energy needs, while the coral provides the algae with a protected environment and access to metabolic waste products.
Keeping Red Green Eye Favia Healthy.
Fascination Favia corals are considered moderately easy to care for. Some experience might be helpful due to the diversity in the group. They are resilient to moderate changes in water parameters but sensitive to sudden fluctuations. They can be aggressive towards nearby corals, using sweeper tentacles to sting competitors.
Light Level.
Red Green Eye Favia corals are not as fussy as some coral so can grow in a wide range of conditions. They do well under moderate light levels. It’s best to start them in lower light and gradually increase exposure so as not to over expose them. If given too much light then the coral will expel zooxanthellae to compensate. In the worst case, this can lead to bleaching.
Corals will react differently under different light intensities and under different spectrums, and colour can be impacted. Feel free to ask for advice.
Flow Rate.
Moderate water flow is ideal, ensuring debris removal without damaging the Red Green Eye Favia coral.
Feeding.
While they obtain most nutrients from their symbiotic algae, Favia corals benefit from occasional feeding with small meaty foods like brine shrimp or plankton, delivered directly to their polyps with a pipette.
All our corals are fed on Coral foods such as, amino acids and plankton. Target feeding with a pipette or coral feeder helps ensure the food reaches the polyps directly.
Reproduction.
1) Sexual Reproduction.
Most corals engage in sexual reproduction through a process known as spawning. During spawning events, corals release eggs and sperm into the water column simultaneously. This typically occurs in a synchronized manner, often triggered by environmental cues such as temperature changes, moon phases, and day length. The synchronization maximizes the likelihood of fertilization.
2) Asexual Reproduction.
One common form of asexual reproduction in corals is budding, where new polyps bud off from parent polyps. This process can occur within the same colony, helping it grow and expand.
3) Importance of Reproduction in Coral Ecology.
Coral reproduction is crucial for the maintenance and expansion of coral reefs. Sexual reproduction introduces genetic diversity, which enhances the resilience of coral populations to environmental stressors such as climate change, diseases, and bleaching events. Asexual reproduction allows for the rapid expansion of colonies and the repair of damaged areas within a reef.
Summary
Red Green Eye Favias are beautiful brain corals. They feature clusters of large, green centered polyps, that are deep set in bright red rings. Even though Favias are easy to look after and suitable for beginners, some consideration should be taken when placing them. Red Green Eye Favias do well in low to moderate light and flow conditions. These corals host photosynthetic algae but can be supplemented with a variety of foods, providing they are small enough to handle. Favias can accept frozen foods, such as mysis, or vitamins/ amino acids.
Dry Goods Delivery.
The store has provided information regarding their order dispatch and estimated delivery times. Here are the key details:
- Dispatch Timeframe: Orders placed before 2pm will be dispatched on the same day. Orders placed after 2pm will be dispatched on the next working day.
- Delivery Date and Time Guarantee: While the store aims to dispatch orders promptly, they cannot guarantee a specific delivery date and time. As the delivery process relies on couriers, there may be factors beyond their control that could affect the delivery timeframe.
- 1st Class Mail: For orders sent via 1st Class mail, the aim is to have them delivered on the next working day after dispatch.
- 2nd Class Mail: Orders sent via 2nd Class mail typically take approximately 2-3 working days for delivery after dispatch.
- APC Next Day Delivery: APC Next Day delivery is available for UK mainland postcodes. It is usually delivered on the next working day after dispatch. However, please note that items being delivered to more remote areas may require additional time for delivery.
It’s important to keep in mind that while the store strives to provide efficient delivery services, unforeseen circumstances or external factors could potentially impact delivery times. For further details or specific inquiries about delivery, customers should refer to the store’s terms and conditions or contact the store directly.
Livestock Delivery.
The store maintains specific policies regarding the delivery of livestock. Here are the key points:
- Licensed Livestock Courier: The store exclusively uses a licensed livestock courier for shipping fish and coral. This approach is chosen to ensure responsible and ethical transportation of the livestock.
- Livestock Shipping Fee: The livestock shipping fee charged to customers of £19.99 does not cover the true cost, and therefore, there is a minimum spend requirement of £30.00 before the option for livestock shipping becomes available.
- Pre-Arranged Delivery: The store never ships livestock without first arranging a suitable delivery day. Before dispatching the livestock, the store must confirm the agreed-upon delivery day with the customer.
- Saturday Delivery Confirmation: Customers who choose Saturday delivery must have their availability confirmed for the upcoming Saturday before the store sends out the livestock. This confirmation ensures that the livestock can be received promptly.
- Failure to wait for livestock: Not waiting for livestock, even if there is a reasonable delay, or cancelling an order after it has been dispatched will lead to you incurring charges for an emergency return to the base. Additionally, any losses of livestock will also be charged to you. Please be aware that the items you are ordering are living creatures – livestock. We kindly ask that you refrain from ordering livestock if you are unable to accommodate the possibility of a delayed delivery.
These terms and conditions are a fundamental aspect of our policy. Our primary goal is to dissuade individuals who could react negatively to a delayed delivery and subsequently request order cancellations. It is of utmost importance to underscore that your order pertains to living creatures, not mere inanimate objects. In the event of an occasional delay, it is crucial that you respond in a rational and responsible manner, taking into account the welfare of the livestock. We kindly request that you refrain from placing an order for livestock if you tend to react strongly to such situations. By proceeding with the order of livestock, you indicate your acceptance and agreement to abide by these specified terms and conditions.
- Signature Requirement: Livestock deliveries require a signature upon receipt and cannot be left in a safe location. This precaution ensures proper handling and the well-being of the livestock.
- Geographic Restrictions: The courier has strict geographic restrictions for livestock deliveries. Unfortunately, deliveries to Northern Ireland, Republic of Ireland, Isle of Man, Isles of Scilly, Channel Islands, and certain Scottish offshore postcodes may not be possible. Customers are encouraged to contact the store via email to confirm if livestock delivery is available in their area.
- Minimum Order Value and Order Cancellations: The store has a minimum order value of £30 for livestock shipping. Additionally, the store reserves the right to cancel orders that are deemed high-risk or involve a high number of single tropical freshwater fish species.
It is essential for customers to familiarize themselves with these policies before making a purchase. For more detailed information or specific inquiries, customers should consult the store’s terms and conditions or reach out to the store directly for clarification.
Livestock Geographical Exemptions.
The store has specific geographical exemptions for livestock deliveries. Here is a list of the areas and postcodes where livestock delivery is not available:
- Islands: Livestock cannot be delivered to the Shetlands, Channel Islands, and Isle of Man.
- Postcodes: Livestock delivery is not available to the following postcodes:
- AB30 to AB39, AB41 to AB45, AB51 to AB56
- DD8 to DD10
- BT all
- DG3 to DG9, DG12 to DG14
- KA18 to KA19, KA26, KA29 to KA30
- HS all
- IM all
- JE all
- ZE all
- KW15 to KW17
- TD9
- FK17 to FK21
- GY all
- KA26, to KA28
- PA20 to PA38, PA41 to PA49, PA60 to PA61, PA76 to PA78
- TR21, to TR25
- PH3 to PH26, PH30 to PH44
- IV all
Customers residing in these areas should be aware that livestock delivery is not available to their location.
We can ship livestock to the Isle of Wight, this area is subject to a surcharge.
For further information or specific inquiries about livestock delivery to a particular area, customers are advised to contact the store directly for clarification.
Cancellation.
According to the store’s policy, customers have the right to cancel an order within 14 working days of receiving the goods. To initiate the cancellation, the goods must be returned to the store in new and unused condition, adhering to their Returns Policy.
Important points regarding the return process are as follows:
- Return Condition: The goods must be returned in new and unused condition, as originally received. It is important to ensure that the goods are in the same condition as when they were sent out.
- Return Timeframe: The goods must be received by the store within 21 days of notifying them about the cancellation. During this time, customers are responsible for any loss or damage that may occur during the return shipping process.
- Refund Process: Once the store receives the goods in new and unused condition, they will initiate the refund process. The purchase price will be refunded to the customer.
- Return Condition Inspection: If the returned goods arrive in a condition that is less than what they were sent out in, the store reserves the right to return the goods to the customer, and no refund will be processed.
It is essential for customers to carefully review the store’s Returns Policy and follow the specified procedures to ensure a smooth and successful return and refund process. For more detailed information or specific inquiries, customers should consult the store’s terms and conditions or contact the store directly.
Returns.
According to the store’s return policy, the following guidelines should be followed for returning goods:
- Use Returns Form: Customers need to use the store’s provided returns form to initiate the return process. This form helps the store acknowledge that the goods are being sent back.
- Return for Testing: If the goods are being returned for testing, the customer is responsible for covering the return shipping expenses.
- Refund of Postage Fees: The store will only refund postage fees if the order arrives damaged or becomes faulty within the first 4 weeks of purchase. Proof of posting is important, and customers should ensure the goods are well-packed and obtain proof of posting as the goods remain their responsibility until received by the store.
- Refund of Postage Costs for Replacement: If goods are being returned within 7 days of purchase under the Replacement Policy, the store can refund postage costs. However, the customer needs to agree on a delivery service with the store in advance, and only standard or tracked shipping fees will be refunded. The store cannot refund the cost of any special delivery service.
- Non-Refundable Postage: Postage costs for goods returned for any other reason than those mentioned above are non-refundable. The store reserves the right to deduct the original postage cost from any applicable refund.
- Mistaken Purchases: If a customer has made a mistake in their purchase, they need to return the goods to the store. The customer is responsible for the return shipping costs in such cases.
It is important for customers to carefully follow the store’s return procedures and terms and conditions. For further details or specific inquiries, customers should refer to the store’s website or contact the store directly.
Replacements
If customers receive faulty goods, the following guidelines apply according to the store’s policy:
- Notification of Faulty Goods: Customers must notify the store within 7 working days if they receive faulty goods. This notification should be made as soon as possible.
- Replacement Parts: If possible, the store will dispatch replacement parts for the faulty goods.
- Return of Goods: If replacement parts are not possible, the store may request customers to return the faulty goods in accordance with their Returns Policy. The specific return procedures and conditions should be followed.
- Verification of Damage: Once the store receives the returned goods, they will verify the damage. If the damage is confirmed, the store will supply the required replacements.
- Return Postage Costs: If the goods returned to the store are found to be in good working order, the store is not able to refund the return postage costs. Additionally, the store reserves the right to deduct their original postage cost from any applicable refund.
- Consequential Loss or Damage: The store cannot take responsibility for any consequential loss or damage that arises directly or indirectly from the goods supplied.
Customers should carefully review and adhere to the store’s Returns Policy and procedures for returning faulty goods. For further clarification or specific inquiries, customers should consult the store’s terms and conditions or contact the store directly.
Manufacturer’s Guarantees
The store works in collaboration with manufacturers to ensure that their guarantees are honored, and they make their best efforts to resolve issues within the warranty period. The following guidelines apply to refunds and replacements:
- Postage Costs under Manufacturer’s Guarantee: Postage costs can only be refunded if the goods are returned to the store within 7 days of the original purchase, as per the manufacturer’s guarantee.
- Refund of Postage Costs for Faulty Goods: The store will refund postage costs for guarantee/warranty returns only if the product becomes faulty within the first 4 weeks of receipt.
- Replacements with Manufacturer Authorization: Replacements, whether parts or goods, can only be offered when authorized by the manufacturer. Customers should contact the store for further guidance in such cases.
- Prior Approval for Returns: Goods should not be returned to the store without prior approval. Customers need to contact the store and obtain approval before returning any items.
- Replacement of Glass or Ceramic Items: Glass or ceramic items can only be replaced if the store is notified within 48 hours of receiving the delivery.
- Replacement of Glass Bulbs/Tubes: Glass bulbs or tubes can only be replaced if they become faulty within 14 days.
Customers should note and adhere to these guidelines to ensure a smooth and efficient resolution of any issues with their purchased items. For specific inquiries or further information, customers are advised to refer to the store’s terms and conditions or contact the store directly.
Breakages
According to the store’s policy, customers have the following responsibilities regarding breakages:
- Checking Goods on Arrival: It is the customer’s responsibility to thoroughly check the goods upon arrival for any damage. This should be done before signing for the parcel. If the parcel appears damaged, it is advised not to sign for it.
- Reporting Breakages: Any breakages or damages must be reported to the store within 48 hours of receiving the goods. It is important to promptly notify the store to initiate the resolution process.
By carefully inspecting the goods upon arrival and reporting any breakages within the specified timeframe, customers can ensure that appropriate actions are taken to address the issue. For specific instructions on reporting breakages or further information, customers should refer to the store’s terms and conditions or contact the store directly.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.